Secreted tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase as a primary defence system against infection.
| Ahn YH, Park S, Choi JJ, Park BK, Rhee KH, Kang E, Ahn S, Lee CH, Lee JS, Inn KS, Cho ML, Park SH, Park K, Park HJ, Lee JH, Park JW, Kwon NH, Shim H, Han BW, Kim P, Lee JY, Jeon Y, Huh JW, Jin M, Kim S |
Abstract
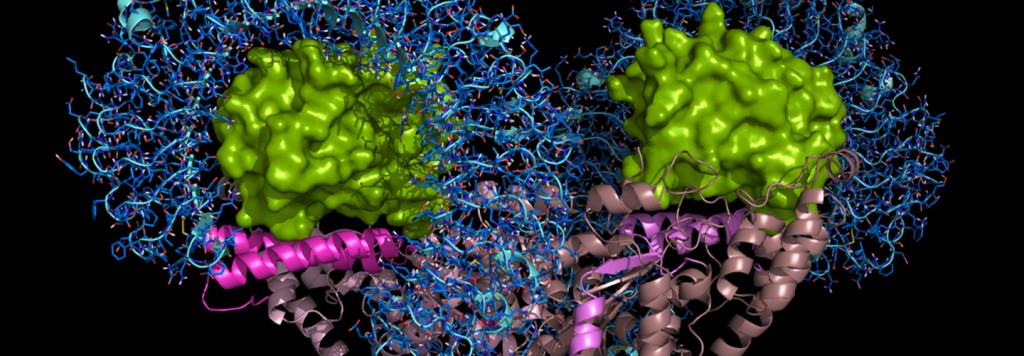
The N-terminal truncated form of a protein synthesis enzyme, tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (mini-WRS), is secreted as an angiostatic ligand. However, the secretion and function of the full-length WRS (FL-WRS) remain unknown. Here, we report that the FL-WRS, but not mini-WRS, is rapidly secreted upon pathogen infection to prime innate immunity. Blood levels of FL-WRS were increased in sepsis patients, but not in those with sterile inflammation. FL-WRS was secreted from monocytes and directly bound to macrophages via a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2) complex to induce phagocytosis and chemokine production. Administration of FL-WRS into Salmonella typhimurium-infected mice reduced the levels of bacteria and improved mouse survival, whereas its titration with the specific antibody aggravated the infection. The N-terminal 154-amino-acid eukaryote-specific peptide of WRS was sufficient to recapitulate FL-WRS activity and its interaction mode with TLR4-MD2 is now suggested. Based on these results, secretion of FL-WRS appears to work as a primary defence system against infection, acting before full activation of innate immunity.
